Table of Contents
In the created revolution, telehealth and remote patient monitoring are the two most vital interventions rewriting the realms of care delivery and experience. In the ever-evolving healthcare landscape, a new era is being scripted where technology meets compassion. Innovation is pushing today’s health care with the most profound changes. Recent research underlines the striking increase in telehealth usage by 38% during the pandemic, while the projection is to see remote monitoring expand at a CAGR of 25.8% through 2027. Such technologies are not only making healthcare better but are revolutionizing how services can be more easily accessible, efficient, and personalized in different ways. [Source- McKinsey & Company, Grand View Research]
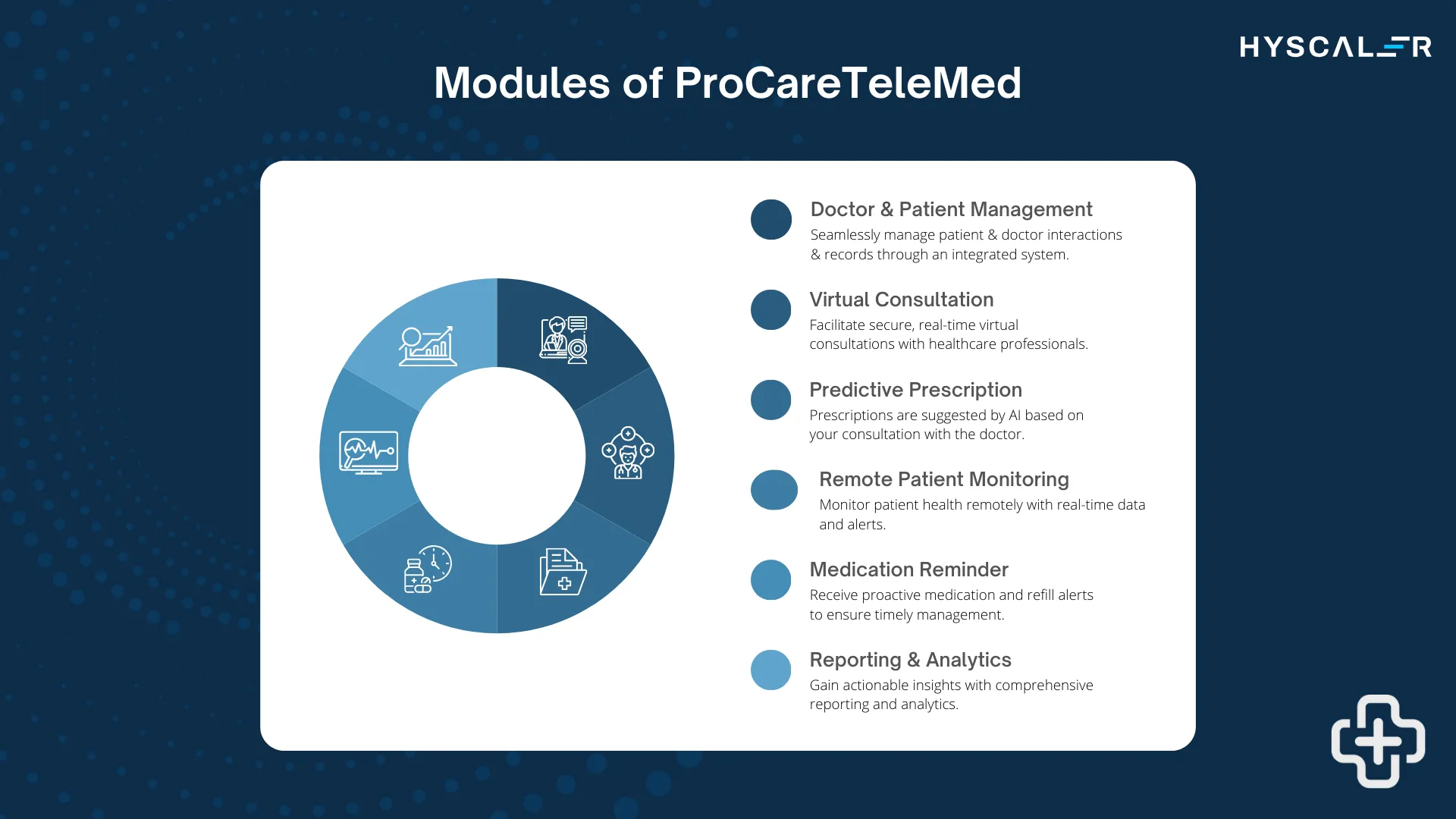
At Hyscaler, we have developed ProCareTeleMed, a comprehensive telemedicine platform that goes beyond standard telehealth functionalities to transform care delivery. This AI-powered, fully HIPAA-compliant platform enhances clinical decision-making with AI-driven consultation notes and proactively identifies potential allergies to ensure safer, personalized treatments.
ProCareTeleMed offers remote patient monitoring for real-time health tracking, providing continuous patient support beyond traditional care settings. Its features—such as medication reminders, refill alerts, and virtual symptom tracking—promote medication adherence and reduce administrative burdens on providers.
Explore more at: https://procaretelemed.com/
Top Trends and Advantages of Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring
Increased Adoption and Convenience: With the growth spurred by the pandemic, telehealth continues to grow in adoption among both patients and providers with virtual consultations growing
Wearable Device Integration: Wearable technology includes smartwatches and fitness trackers, which have gained more use in the setting of remote monitoring systems. These devices provide continuous health tracking, thus opening new opportunities for real-time data to support better chronic disease management and personalized care.
AI and Machine Learning: This has been a major application area for AI-powered tools, which have been offering a set of predictive analytics and automated solutions. These technologies improve patient outcomes by making personalized suggestions for better care and administrative processes.
Improved Data Security: With the use increases for digital health solutions, so does the interest in security and privacy. Strong measures are in place, such as advanced encryption and adherence to regulations similar to HIPAA.
Cost Savings and Efficient Resource Utilization: Both patients and providers benefit from reduced costs associated with telehealth. Savings come from fewer in-person visits, lower travel expenses, and optimized healthcare resource management.
AI in Remote Patient Monitoring and Telehealth: Application Statistics
1. Growth of AI for Remote Patient Monitoring
The adoption of artificial intelligence in remote patient monitoring is growing massively because of the global influence of telehealth. The different AI models implemented over RPM aided in the monitoring of chronic conditions and prediction of health risks with real-time alerts. In 2023, the size of the AI-driven RPM market was estimated to value approximately $1.1 billion and is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 26% between 2024 and 2028.
2. Applications of AI in Telehealth
- Predictive Analytics for Patient Outcomes: AI models such as CNNs and random forests are particularly popular, where such algorithms are being used to predict the outcomes of patients, especially in the management of chronic diseases. In some cases of telehealth, they have been shown to reduce hospital readmissions by over 30%.
- Personalized Care Recommendations: AI-driven systems analyze patient data to provide personalized treatment recommendations. This indeed has been linked to a 20% increase in adherence to prescribed treatments by patients.
- Automated Diagnosis: For instance, AI algorithms, such as those based on Support Vector Machines, help in the diagnosis of conditions from medical imaging and sensor data. Regarding this, diagnostic errors have decreased by about 40%.
3. AI-Powered Virtual Health Assistants
AI-powered virtual assistants are being introduced that can help in basic consultations for patients, symptom checks, and medication reminders. A few studies mention that AI assistants have helped doctors reduce their workload by up to 50% in a telemedicine setting, yet provided more than 90% patient satisfaction.
4. Management of Chronic Diseases
AI-enabled RPM has emerged in the management of chronic diseases to improve outcomes in the management of diabetes, heart failure, and COPD by approximately 25%, with a reduction in healthcare costs by 15-20% through proactive monitoring and interventions.
5. Telemedicine Adoption Statistics: By 2023, over 70% of healthcare providers were already on the use of some form of AI in their telehealth platforms, and this is likely to increase further with increasing demand for remote healthcare services. AI-powered triage systems cut queues for telemedicine consultations by an average of 60%, ensuring access to care much more quickly.
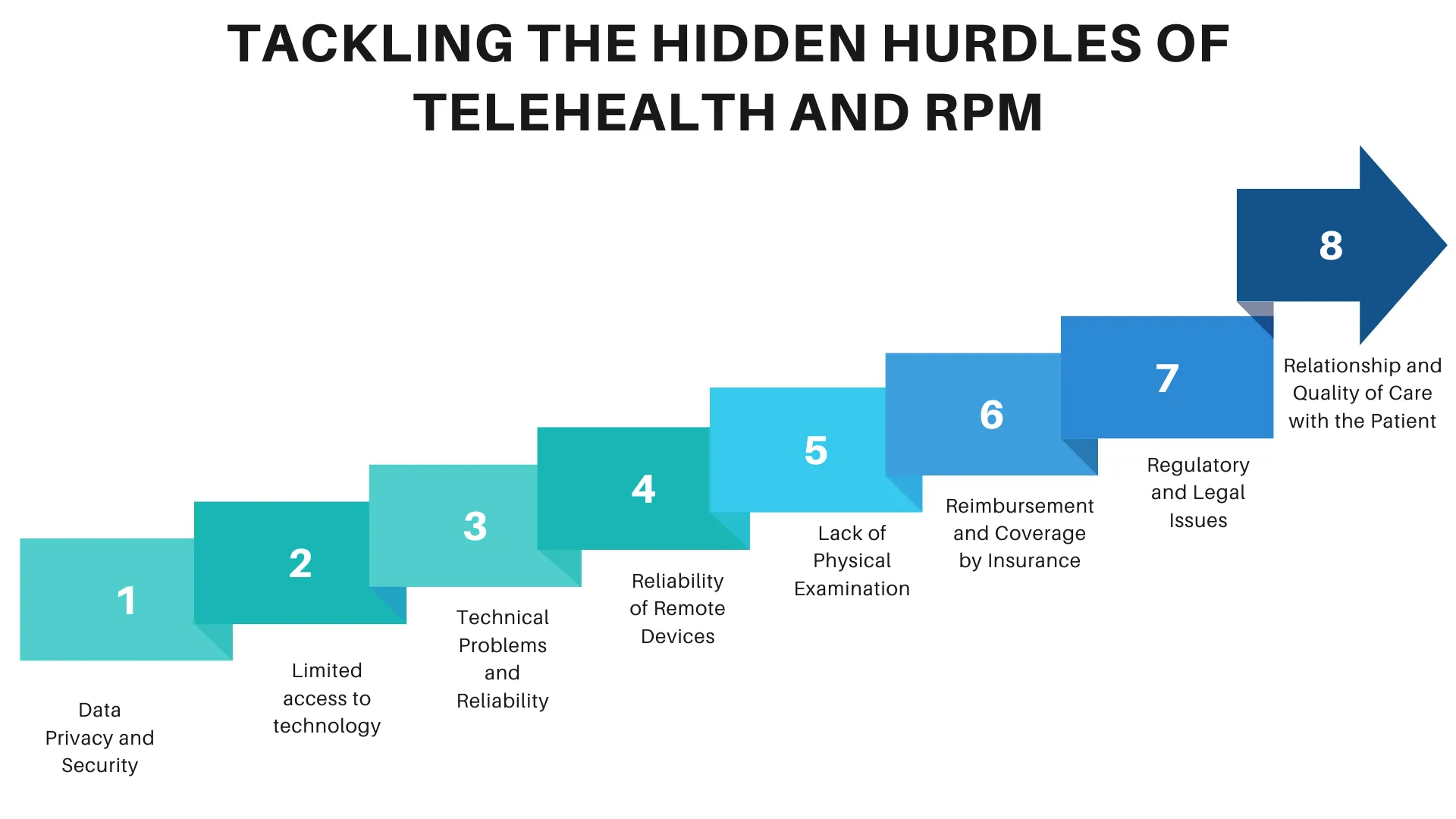
Tackling the Hidden Hurdles of Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring
Data Privacy and Security: The amount of sensitive patient information telehealth and telemonitoring necessitates collection as well as transmission and raises significant concerns about ensuring that such information is safe from breaches and cyberattacks since HIPAA imposes stringent regulations and healthcare organizations expose themselves to potential enforcements under each or a combination of these areas.
Limited access to technology: Not all patients have the required technology, such as phones, intact internet, or wearables. This digital divide limits telehealth at times, especially in underdeveloped, diverse, or rural areas.
Technical Problems and Reliability: Technical problems such as connectivity issues, software bugs, or a defective device may lead to interrupted remote monitoring and telehealth sessions. This could allow partially conducted consultations and may even impact patient care.
Reliability of Remote Devices: The remote devices used in monitoring should display correct and reliable information. Incorrect measurements may lead to improper diagnoses or, worse, unmonitored health problems – hazardous to the patient’s health.
Lack of Physical Examination: Perhaps the main disadvantage of telehealth is that it significantly limits the ability of the healthcare provider to carry out hands-on, physical examination. When a condition or symptom is not appropriately identified or diagnosed because a direct physical assessment of the patient has not been carried out, the quality of service suffers.
Reimbursement and Coverage by Insurance: Policy variations additionally cover reimbursement and insurance, which does not necessarily cover telehealth consultations or remote monitoring. This deters providers from using this technology and also deters patients from utilizing it.
Regulatory and Legal Issues: Telehealth and remote monitoring will have to follow rules that can differ by state. Cross-cutting issues like licensure and cross-state practice laws are also regulated differently, which is pretty challenging for healthcare professionals.
Relationship and Quality of Care with the Patient: It is more difficult to create a relationship in the virtual field with the patient. Physical contact, which leads to face-to-face communication minimization, affects the quality of care and patient satisfaction.
How Telehealth and RPM Tackle Key Challenges
- Bridging the Gaps in Accessibility: Telehealth removes the barriers of distance and transportation, making healthcare accessible to patients residing in remote or underserved areas. This guarantees timely medical consultations and reduces disparities in access to health care.
- Reducing Patient Wait Times: Virtual consultations streamline appointment scheduling and reduce wait times, offering quicker access for patients to healthcare services and alleviating in-person clinic strain.
- Improve Management of Chronic Diseases: Remote monitoring devices track vital signs continuously, like blood glucose levels and heart rates. They have allowed for the proactive management of chronic diseases with timely interventions.
- Improved Patient Engagement: Through digital health solutions, patients are put at the center by having easy access to health data, educational resources, and personalized care plans; through increased engagement, adherence to treatment and health improvement are achieved.
- Reduction in administrative and operational costs: Telehealth reduces the need for physical infrastructure and lowers travel and other administrative expenses, thereby fostering more resource-efficient and inexpensive services for healthcare professionals and patients.
- Data security: By focusing on strong data protection measures in compliance with regulations like HIPAA, telehealth and remote monitoring technologies ensure a guarantee for the protection of patient information in secure confidence.
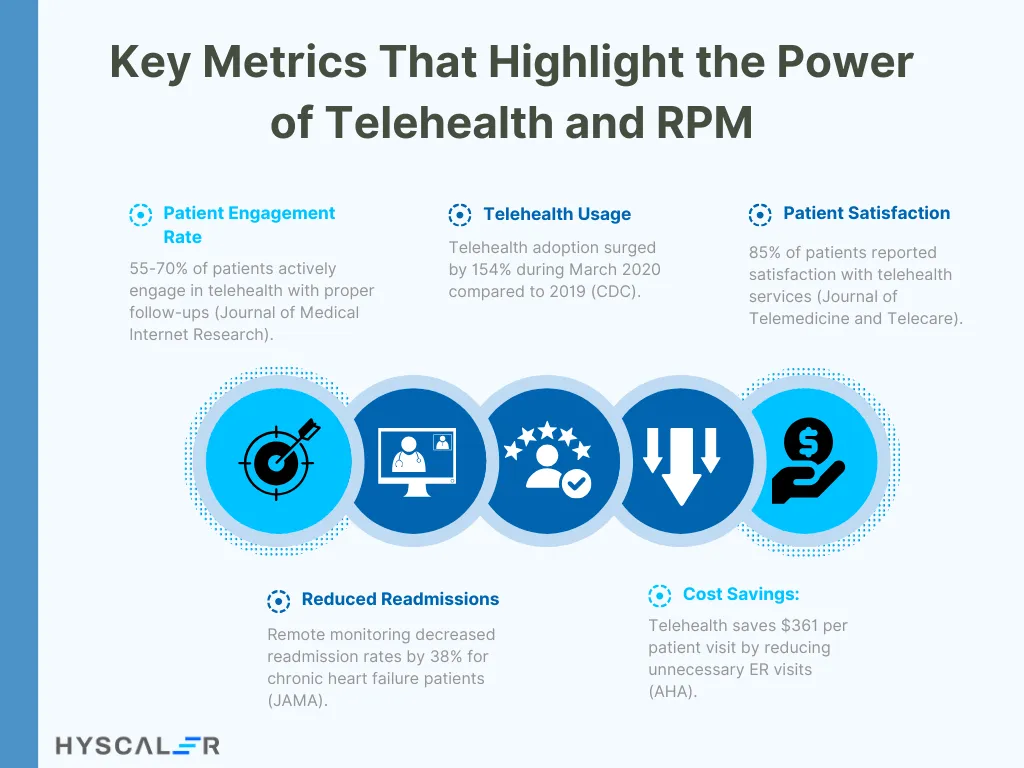
Key Metrics That Highlight the Power of Telehealth and RPM
Patient Engagement Rate: This measures the level of engagement of patients in the utilization of telehealth services and use of remote monitoring devices. “A systematic review of studies reveals that active participation rate among patients in telehealth programs stands at 55 to 70% provided the facility of follow-up and easy-access portals,” postures one study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research.”
Telehealth Usage Rate: According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the utilization of telehealth increased by 154% in the last week of March 2020 relative to the same period in 2019. That means the uptake and implementation of telehealth services are developing relatively fast within healthcare systems.
Patient Satisfaction Score: This relates to the level of patient satisfaction with service delivery using telemedicine, which is commonly measured using a questionnaire. The Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare has reported that, on average, 85% of its telehealth services recorded a satisfaction score, and thus, most patients are embracing and have developed a positive perception of telemedicine.
Reducing readmissions: Certainly, the efficacy of RPM was seen through a decrease in readmission rates. According to the Journal of the American Medical Association, researchers found that 38% of patients who experience chronic heart failure had decreased readmission with the use of remote monitoring.
Cost savings: According to the American Hospital Association, telehealth programs may reduce the cost by $361 per patient visit from unwarranted emergency room visits and hospital admissions.
The Transformative Future of Telehealth and RPM
The future of telehealth and remote monitoring will witness complex AI in personalized care, better wearables to provide real-time health data, and increased access through better connectivity. Integration with EHRs will therefore be streamlined in data sharing. Enhanced security measures will protect patient information. Innovations like VR and AR will make remote consultations even more immersive, and all such medicine will be centered on personalization. Evolving regulations and a mental health focus will be the forces driving improvement in both the quality and access to care. Curious about how these advancements can transform practices? Let’s explore the possibilities together and unlock the future of healthcare.